In the Covenant that we use in our process of re-assembling the states of America, it is written that the common law of the people is the expression of “Scripture of all stripes”. This common law is the common law of the people, as opposed to The Common Law of England, or any other form of common law. The common law of the people is sometimes referred to as Anglo-Saxon common law, which was the law of England from the 6th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. It was a combination of Germanic law, royal decrees, and traditional practices that governed many aspects of life. To the extent that Anglo-Saxon common law was consistent with Scripture, which we define in the Covenant as “Direct Divine Revelation”, it can be considered as being the common law of the people. For those who wish to take a deeper dive into this, click on the link below, and use your discernment to judge how consistent it was with Scripture.
Read More ...
Abuses by King John caused a revolt by nobles who compelled him to execute this recognition of rights for them, the Barons and their families. We were all misled in to thinking that it was a legal or lawful authority and even that it provided the basis for modern day Grand Juries and Trial by Jury. However, Magna Carta never had any legal effect, as it was rejected by the Pope, partly due to the fact that King John was forced to sign it, and partly, as the Pope stated in a letter to King John, because all human rights are contrary to the tenets of the Church.
To learn more about this, investigate each of the following links:
Hammurabi to Common Law
The Beginning of the Lie
Magna Carta by John Harris (An Englishman's explanation)
Magna Carta and Trial By Jury
Read the Magna Carta
The Iroquois Constitution, also known as the Great Law of Peace or Kaianere'kó:wa in Mohawk, served as the oral constitution of the Iroquois Confederacy. It was created to organize Iroquois society and establish a representative form of government between the five Iroquois-speaking tribes that formed the Confederacy around 1450: Seneca, Cayuga, Oneida, Onondaga, and Mohawk. As a representative form of government, it is an early example of what was meant in the Constitution for the United States of America, where a “Republican form of government” is guaranteed to the American states of the Union. A “Republican form of government” is, according to the generally accepted definition expressed by James Madison in the Federalist Papers, a form of government where the body politic (the electors) elect representatives to make laws instead of the people directly voting on laws.
Read More ...

History and Legacy: It was the Geneva Bible that accompanied our forefathers to the new world. They made history in many ways, not the least of which was a legacy of Scriptural wisdom inspired by the Geneva Bible.
Read More ...
The Virginia Company was an English trading company chartered by King James I on 10 April 1606 with the objective of colonizing the eastern coast of America. The coast was named Virginia, after Elizabeth I, and it stretched from present-day Maine to the Carolinas.
The Mayflower Compact, originally titled Agreement Between the Settlers of New Plymouth, was the first governing document of Plymouth Colony. It was written by the men aboard the Mayflower, consisting of Separatist Puritans, adventurers, and tradesmen.
The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut was a document that served as the framework for the Connecticut Colony's government from 1639 to 1662. It's made up of a preamble and 11 "orders" (or laws) that established a representative government based on the example of Massachusetts colonies. The document is considered by some to be the first written constitution in western democratic tradition.
In 1791, the constitutionality of the Bank of the United States was debated in the House of Representatives. Alexander Hamilton, the first Secretary of the Treasury under George Washington, supported the bank's constitutionality, arguing that the Constitution should be interpreted broadly to allow the government to function properly. Hamilton believed that the government has the power to act unless it is explicitly prohibited from doing so, and that the power to incorporate a bank was an ordinary power that was incidental to the government's regular powers. He also argued that the power to erect corporations is inherent in sovereign power and should be implied rather than expressly granted.
Emmerich de Vattel (1714-67) was the author of The Law of Nations (1758). Swiss-born Vattel’s most famous work consisted of the application of the law of nature to nations. He understood the law of nature as accessible by human reason, according to which both individuals and political societies are capable of understanding their rights and obligations. Introduced into the American colonies in the 1760s, Vattel’s teachings about international law and sovereignty were not only carefully studied by American statesmen but applied by them in the international arena.
In 1776, North Carolina's Fifth Provincial Congress created a state constitution meant to support North Carolinians in their fight for American independence. Several other foundational documents are also associated with the North Carolina Constitution of 1776, including the Declaration of Rights of 1776 and the Ordinances of the Convention. The Declaration of Rights provided for the basic rights of North Carolinians, including popular sovereignty, separation of powers, and freedom of religion. The Ordinances of the Convention was used in conjunction with the state constitution to provide for the basic legal structure of North Carolina's government.
The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America, When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.

The primary purpose of the Articles of Confederation was to establish a national government for the newly independent United States after the American Revolution, acting as the first constitution by outlining a loose union of states while preserving the sovereignty of each individual state, allowing them to function as a unified nation while maintaining their independence; however, due to its design, the central government had very limited power under the Articles.
The United States Constitution was written and signed in 1787, not 1776. The Declaration of Independence was written and adopted in 1776, however, and is a separate document from the Constitution.
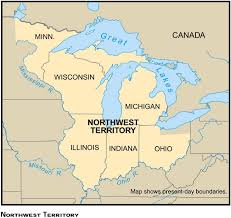
The Northwest Ordinance of 1787 was a law that established the government for the Northwest Territory, outlined the process for admitting new states, and guaranteed a bill of rights for the territory. The ordinance was passed on July 13, 1787.
Read More ...

The Bill of Rights is the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution. It spells out Americans’ rights in relation to their government. It guarantees civil rights and liberties to the individual—like freedom of speech, press, and religion. It sets rules for due process of law and reserves all powers not delegated to the Federal Government to the people or the States. And it specifies that “the enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people.”
As a result, a Federalist-controlled Congress passed four laws, known collectively as the Alien and Sedition Acts. These laws raised the residency requirements for citizenship from 5 to 14 years, authorized the President to deport aliens and permitted their arrest, imprisonment, and deportation during wartime.

General Order 100, also known as the Lieber Code, was a set of rules that governed the conduct of Union soldiers during the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln issued the order on April 24, 1863. The Lieber Code was named after its main author, Francis Lieber.

The original Amendment Thirteen to the U.S. Constitution was part of why the British attacked us in 1812. This original amendment was not about slavery, but about titles of nobility, like BAR attorneys, for example. Knowledge of, and enforcement of, this Amendment might have prevented a great deal of the corruption that arose during the course of our history. This has been hidden from the general population until fairly recently.

The Dick Act, also known as the Militia Act of 1903 or the Efficiency in Militia Act of 1903, was a law passed by Congress in 1903 that created the modern National Guard. The act was sponsored by Senator Charles W. F. Dick, a Major General in the Ohio National Guard.

The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States was signed on December 26, 1933, at the Seventh International Conference of American States in Montevideo, Uruguay. The treaty established the definition of a state under international law and went into effect on December 26, 1934.

The Bretton Woods Agreement established a system through which a fixed currency exchange rate could be created using gold as the universal standard. The agreement involved representatives from 44 nations and brought about the creation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
![]()